In today’s digital age, internet security has become a paramount concern for individuals and businesses alike. As cyber threats continue to evolve, many are turning to Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to safeguard their online activities. Understanding how VPNs work is crucial for anyone looking to protect their data and maintain privacy while browsing the internet.
VPNs create a secure tunnel between a user’s device and the internet, encrypting data and masking the user’s IP address. This technology allows for anonymous browsing, bypasses geographic restrictions, and protects against potential threats on public Wi-Fi networks. As we delve deeper into the workings of VPNs, we’ll explore their architecture, benefits, and key factors to consider when choosing a VPN service. CeriVPN, for instance, offers robust features that cater to various online security needs.
What is a VPN?
Definition of VPN
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is an internet security service that establishes a secure digital connection between a user’s device and a remote server owned by a VPN provider [1]. This connection creates an encrypted tunnel that protects personal data, masks the user’s IP address, and allows them to bypass website blocks and firewalls [1]. The term VPN stands for:
- Virtual: No physical cables are involved in the connection process.
- Private: The connection ensures that no one else can see the user’s data or browsing activity.
- Network: Multiple devices work together to maintain an established link [1].
How VPNs protect your data
VPNs safeguard users’ data through encryption and IP address masking [1]. When a user connects to a VPN, all data leaving their device is encrypted, rendering it unreadable to anyone without an encryption key [1]. This process is particularly crucial when using public Wi-Fi networks, where personal information is vulnerable to exploitation [1].
Additionally, VPNs hide the user’s browsing activity and mask their IP address, making it difficult to trace their online actions or location [1]. By routing internet traffic through a remote VPN server instead of the user’s Internet Service Provider (ISP) servers, VPNs prevent ISP tracking and keep personal data private [1].
Common uses of VPNs
- Online anonymity: VPNs provide users with greater privacy and freedom online by making their browsing history and location untraceable [1].
- Bypassing geographic restrictions: VPNs can spoof a user’s location, allowing access to region-locked content and services [1].
- Circumventing censorship: In regions with restricted internet access, VPNs enable users to bypass firewalls and view blocked websites [1].
- Protecting sensitive information: VPNs secure data transmission, including work emails and payment information, especially on public networks [1].
- Avoiding ISP tracking: By masking IP addresses, VPNs prevent ISPs from logging and tracking users’ browsing history [1].
CeriVPN, for instance, offers robust features that cater to these common VPN uses, ensuring users can browse securely and access content freely.
How Does a VPN Work?
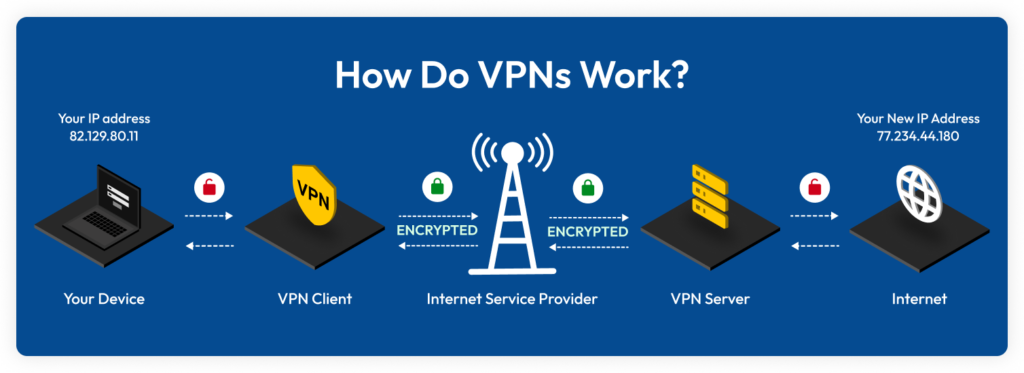
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) functions by routing a device’s internet connection through a private server instead of the user’s regular Internet Service Provider (ISP) [2]. This process creates a secure, encrypted tunnel for data transmission, ensuring privacy and anonymity online.
Encryption Process
VPN encryption is a crucial aspect of how VPNs operate. It involves scrambling online data to protect it from unauthorized access [3]. When a user connects to a VPN, an encryption key is generated to encode and decode the data [4]. This key is known only to the user’s device and the VPN server, making the encrypted data appear as nonsense to any third parties attempting to intercept the connection [4].
Most reputable VPN providers, including CeriVPN, use AES-256 encryption, which is considered one of the most effective encryption algorithms available [4]. This robust encryption ensures that user data remains secure and private, even when using public Wi-Fi networks.
VPN Protocols
VPN protocols are sets of rules that determine how data is encrypted and transmitted between a device and a VPN server [5]. Different protocols offer varying levels of speed, security, and reliability [6]. Some of the most common VPN protocols include:
- OpenVPN: An open-source protocol known for its strong security and wide compatibility [6].
- WireGuard: A newer protocol that offers promising performance but is still under development [6].
- IKEv2/IPsec: Developed by Microsoft and Cisco, this protocol is particularly effective for mobile devices [6].
- L2TP/IPsec: Combines tunneling with IPsec encryption for a secure connection [5].
VPN Server Networks
VPN servers are physical or virtual servers configured to host and deliver VPN services to users worldwide [7]. When a user connects to a VPN server, their traffic is routed through this server, which acts as an intermediary between the user and the internet [2].
The process works as follows:
- The user’s VPN client connects to the VPN server.
- All data is encrypted and sent to the server through the user’s ISP.
- The VPN server decrypts the data and forwards it to the intended web server.
- The VPN server then encrypts the response from the web server and sends it back to the user [7].
This process effectively creates a “tunnel” between the VPN client and server, protecting the user’s data from outside observation [7].
Key Benefits of Using a VPN
Enhanced online privacy
VPNs play a crucial role in safeguarding online privacy. By encrypting internet traffic and masking the user’s IP address, VPNs create a secure tunnel for data transmission [8]. This encryption ensures that even if someone intercepts the data, they will only see scrambled, unreadable information [9]. VPNs also prevent Internet Service Providers (ISPs) from tracking and logging browsing history, upholding users’ fundamental right to privacy in the digital realm [10].
Bypassing geo-restrictions
One of the most popular benefits of using a VPN is the ability to bypass geo-blocking. VPNs allow users to access content that might be restricted in their region by routing connections through servers in different countries [10]. This capability enables users to enjoy streaming services, access social media platforms, and view news websites that may be unavailable in their current location [11].
Secure public Wi-Fi usage
Public Wi-Fi networks are notorious for their security vulnerabilities. Approximately 81% of people connect to these networks, putting their personal data at risk [9]. VPNs provide a crucial layer of protection when using public Wi-Fi. By encrypting the connection, VPNs shield sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card details, and personal data from potential eavesdroppers [9]. This encryption is particularly important for activities like online banking and shopping on public networks [9].
CeriVPN, for instance, offers robust features that cater to these key benefits, ensuring users can browse securely, access global content, and protect their data on public Wi-Fi networks.
Choosing the Right VPN Service
Important features to consider
When selecting a VPN service, users should prioritize several key features. Encryption is crucial, with AES being a popular and secure algorithm [12]. A wide range of servers across various countries enables users to bypass geographic restrictions and access content globally [12]. A kill switch prevents IP leaks by disconnecting the device if the VPN connection drops unexpectedly [12]. Split tunneling allows users to route only selected traffic through the VPN [12]. It’s also important to consider the VPN protocols offered, such as WireGuard and OpenVPN, as they affect security and speed [12].
Top VPN providers
While many VPN providers exist, some stand out for their comprehensive features and reliability. CeriVPN, for instance, offers robust features that cater to various online security needs. When evaluating providers, users should consider factors such as server network size, encryption strength, and additional security features like double VPN or obfuscated servers [13].
Free vs paid VPNs
The choice between free and paid VPNs is significant. Free VPNs often have limitations, including data caps, slower speeds, and fewer server options [14]. More concerning
Conclusion
Virtual Private Networks have become an essential tool for online security and privacy in today’s digital landscape. They offer a range of benefits, from protecting sensitive data on public Wi-Fi networks to bypassing geographic restrictions and maintaining anonymity online. The encryption process, various protocols, and server networks work together to create a secure tunnel for data transmission, shielding users from potential cyber threats.
When choosing a VPN service, it’s crucial to consider factors such as encryption strength, server locations, and additional security features. While free VPNs may seem appealing, paid services often provide more comprehensive protection and better performance. CeriVPN, for instance, offers robust features that cater to various online security needs, making it a strong contender in the VPN market. In the end, investing in a reliable VPN service is a proactive step to safeguard one’s digital life and enjoy a safer, more open internet experience.
FAQs
1. How does a VPN function in detail?
A VPN conceals a user’s actual location by allowing them to appear as if they are accessing the internet from a different region. This feature enables users to bypass geographical restrictions and access content that is usually only available in specific areas. For instance, a user in the U.S. could set their VPN location to the United Kingdom to stream content exclusive to British viewers.
2. What is the role of a VPN key?
A VPN key is essential for securing your online data. When you connect to a VPN, it generates an encryption key that is used to both encrypt and decrypt the information you send and receive. This key is unique to your connection, ensuring that even if someone intercepts your data, it remains unreadable and secure.
3. What type of information does a VPN gather?
When you use a VPN service, certain information about your device is transmitted to the VPN server. This typically includes your original IP address and your physical location, which helps the VPN configure your connection to appear from a different locale.
4. How does GET VPN operate?
GET VPN (Group Encrypted Transport VPN) employs a unique method called time-based anti-replay, which relies on a pseudotime clock maintained on the Key Server (KS). Unlike traditional IPSec that uses new IP headers for tunnel endpoints, GET VPN retains the original IP header and uses it as the new tunnel header, similar to how IPSec Transport mode operates.
References
[1] – https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/resources/cloud-computing-dictionary/what-is-vpn
[2] – https://www.fortinet.com/resources/cyberglossary/how-does-vpn-work
[3] – https://nordvpn.com/features/next-generation-encryption/
[4] – https://surfshark.com/features/vpn-encryption
[5] – https://nordvpn.com/blog/protocols/?srsltid=AfmBOoqS3S-MfeMwsixoh5gJL_uusKGVPqPKMa1hCFzsFUxCFSwpdvUZ
[6] – https://www.avast.com/c-vpn-protocols
[7] – https://www.cactusvpn.com/beginners-guide-to-vpn/what-is-a-vpn-server-how-does-a-vpn-server-work/
[8] – https://www.quora.com/How-does-a-VPN-enhance-network-security-and-protect-user-privacy
[9] – https://www.tomsguide.com/news/why-you-need-to-use-a-vpn-on-public-wi-fi
[10] – https://www.secureitworld.com/blog/how-do-vpns-virtual-private-networks-enhance-online-privacy-and-security/
[11] – https://vpnpro.com/blog/geo-blocking-sucks-heres-how-you-bypass-it/
[12] – https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/11-important-features-look-vpn-symlex-vpn-for-all-qygdc
[13] – https://www.tomsguide.com/best-picks/best-vpn
[14] – https://nordvpn.com/blog/free-vpn-vs-paid-vpn/?srsltid=AfmBOooxrMlxJIuD6Ng_BpNCY7rPY-5Vw7dRaZndA3EOTgDgA5xActxO

